Neutron-induced reactions
Virtually all measurements of neutron-induced reactions interesting for nuclear astrophysics are performed
either applying the time-of-flight (TOF) technique or the activation technique. The most important reactions
are neutron captures (n,γ), neutron-induced alpha emission (n,α) and neutron-induced fission (n,f).
A typical TOF setup consists of a pulsed neutron source, a sample positioned at a given flight path and a
time-resolving detection system for the reaction products.
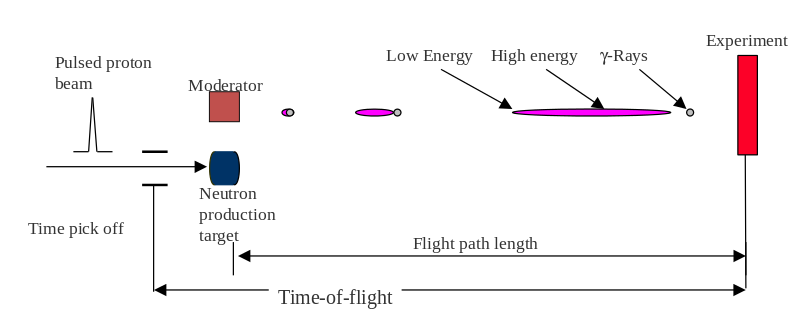
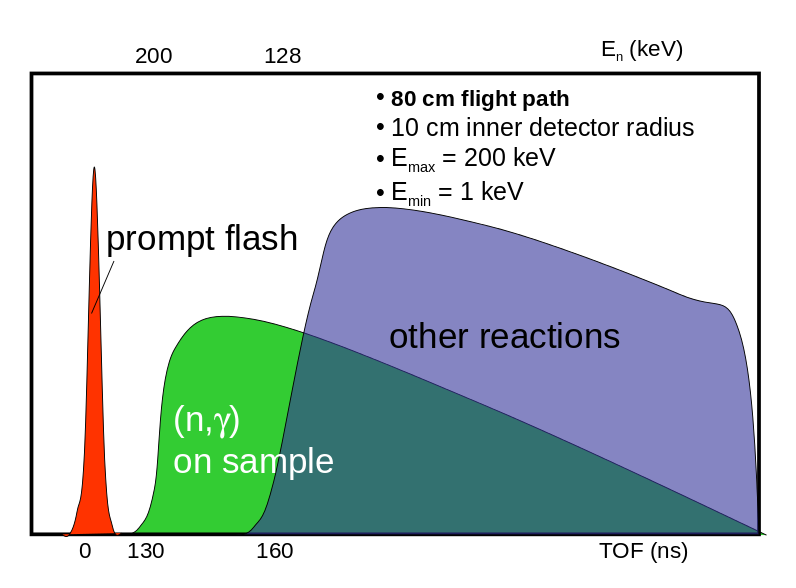
Usually, the TOF-spectrum begins with the γ-flash resulting from interactions of the primary beam particles
with the neutron production target. The gammas traveling at the speed of light arrive first at the detector systems.
Later the first, fastest neutrons arrive and even later slower neutrons.
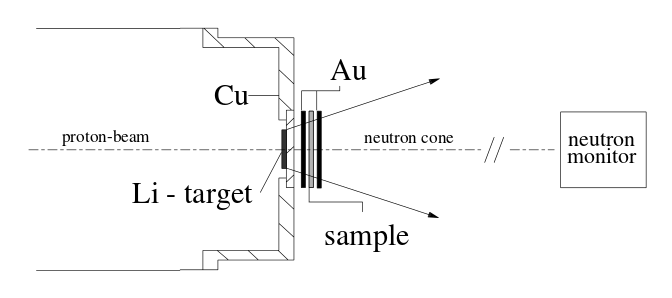
A typical activation setup consists of a continuous neutron source, a sample positioned very close to the
neutron source and a separate setup to detect to decay of freshly produced, radioactive nuclei.
Experiments
FRANZ at Uni Frankfurt
LAND/R3B at GSI
DANCE at Los Alamos
n_TOF at CERN
|