Research
Idea
Nucleosynthesis of the chemical elements during the evolution of stars is the basis for understanding the
chemical history of the Universe. All the elements heavier than iron are produced by neutron capture
reactions. The neutron capture cross sections for certain isotopes constrain stellar parameters on the one
hand, and also lead to strong constraints on the age of the Universe.
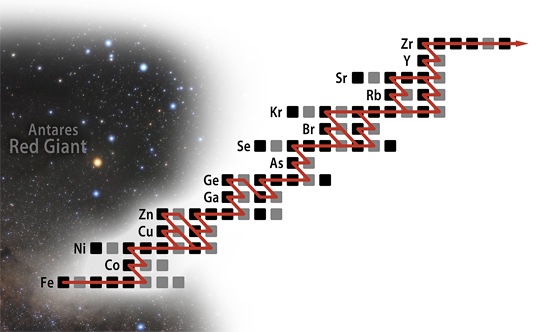
NAUTILUS will focus on investigating a particularly interesting region in the chart of nuclides. Accurate
measurements of the key nuclear reactions in the region around 85Kr will lead to the necessary improvements
for characterizing the production processes of the elements in stars to the point where the respective
abundance patterns can be interpreted as diagnostic tools for the deep stellar interior and the history of the
universe.
Setup
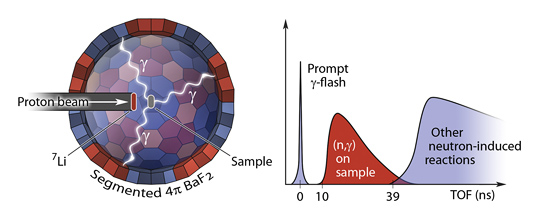
The neutron capture cross section of radioactive isotopes for neutron energies in the keV region will be
measured by a time-of-flight (TOF) experiment. NAUTILUS will provide a unique facility realizing the TOF
technique with an ultra-short flight path at the FRANZ setup at Goethe-University Frankfurt am Main,
Germany. A highly optimized spherical photon calorimeter will be build and installed at an ultra-short flight
path.
Experiments
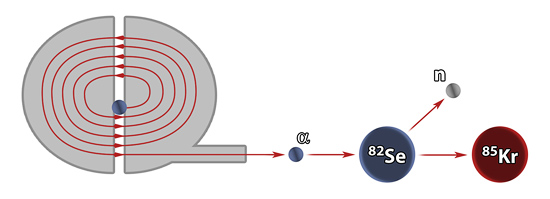
This new method allows the measurement of neutron capture cross sections on extremely small sample
as needed in the case of 85Kr, which will be produced as an isotopically pure radioactive sample.
The successful accomplishment of NAUTILUS will provide insights into the dynamics of the late stages of
stars, an important independent check of the evolution of the Universe and the proof of principle of a new
method determining neutron capture cross section on extremely small samples.