n_TOF - neutron time-of-flight
The neutron time-of-flight facility n_TOF located at CERN enables the measurement of (n,γ) cross sections from
thermal neutron energies to approximately 1 MeV, covering the entire neutron energy range of astrophysical interest.
Neutrons are produced via spallation reactions of highly energetic protons (20 GeV/c momentum) provided by the PS accelerator,
impinging on a massive Pb target. The short proton pulse width of 7 ns and the long flight path of 185 m guarantee a high
neutron energy resolution.
The intensity of a nominal proton pulse is 7e12 protons, producing around 1e15 neutrons at the target station.
This results in a high instantaneous neutron flux despite of the long flight path. Two detection setups are available for
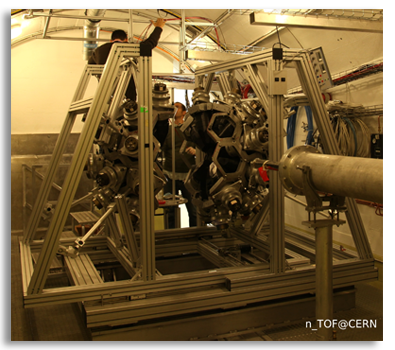
measuring neutron capture cross sections: a 4p detector array (Total Absorption Calorimeter, TAC), consisting of 42 BaF crystals
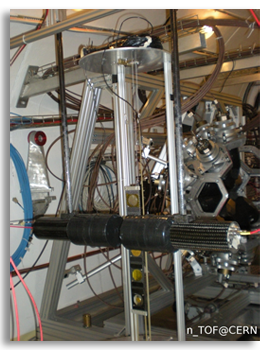
(see figure 1), and a pair of liquid scintillation (C6D6) detectors (figure 2), which are specially optimized for a low sensitivity
to scattered neutrons. Apart from neutron capture, also other neutron induced reactions are studied, e.g. (n,f) and (n,α) reactions.
Recently, a second experimental area at a shorter flight path of ~20 m was commissioned extending the measurement program to
samples with smaller masses (e.g. radioactive samples) and/or smaller cross sections.
More information is available on the following websites:
www.cern.ch/ntof
https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/NTOF/
 |
|
 |
| Total Absorption Calorimeter for (n,γ) measurements |
|
The C6D6 setup for (n,γ) measurements, consisting of a pair of liquid scintillation detectors.
The samples can be placed on a remotely controllable ladder. |
|